Can Optimized Concrete Mixtures Drive Sustainable Construction?
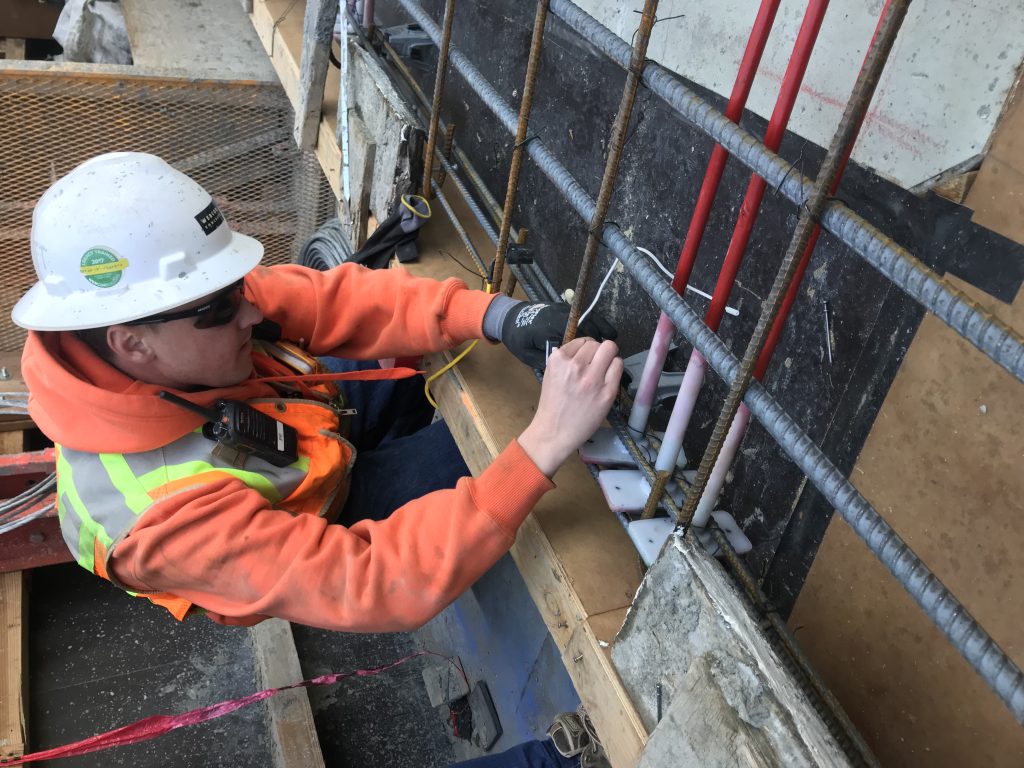
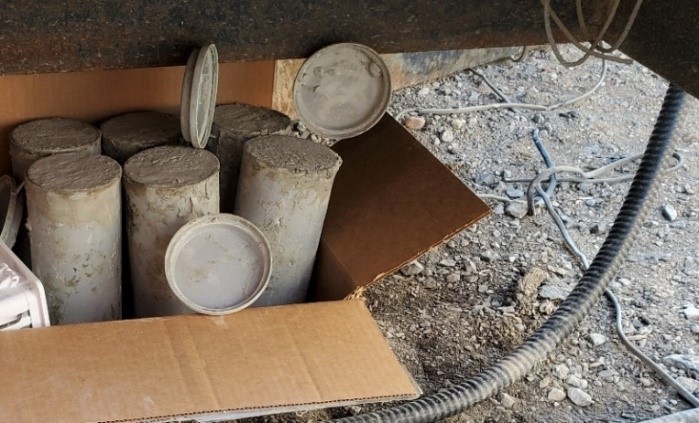
Optimizing concrete mixtures is essential in adapting to evolving sustainability requirements being imposed on ready-mix organizations globally. However, this effort is challenged by several factors including the emergence of new materials, evolving demands, diverse market standards, and limitations in testing practices. This blog explores these challenges and outlines…