No matter where you are in the world, the ability to accurately measure the early age compressive strength of concrete is vital for a wide spectrum of construction projects. Concrete maturity directly affects the structural integrity and safety standards of job sites as well as the speed at which a project can be completed, all of which also impact economic considerations. The more accurately and quickly in-situ compressive strength can be measured, the better contractors and engineers can optimize critical activities such as formwork removal, opening roads to traffic and many more.
Explore 12 Futuristic Technology Trends Solving Concrete's Biggest Challenges.
While measuring concrete strength is one of the most important aspects of construction, general contractors, engineers, and the construction industry as a whole have always struggled with predicting the time needed to reach design strength at a given time.
Concrete Maturity Method Definition
There are several ways to test concrete strength, but the concrete maturity method has emerged to become the champion of concrete strength prediction thanks to its non-destructive nature and ability to provide relevant data quickly and efficiently. This technique can be measured in real-time and is based on the principle that concrete strength is directly related to its hydration temperature history.
Find your next concrete strength solution!
Countries and Regions Where the Maturity Method is Standardized
In our Concrete Maturity eBook, we compiled a list of countries and regions that have different codes and standards for concrete maturity. Take a look at the list below – are you familiar with the standards in your country?
United States
- ASTM C1074: Standard Practice for Estimating Concrete Strength by Maturity Method
- ASTM C918: Standard Test Method for Measuring Early-Age Compressive Strength and Projecting Later-Age Strength
- ACI 318- 6.2: Building Code Requirement for Structural Concrete and Commentary
- ACI 228.1R: In-place Methods to Estimate Concrete Strength
- ACI 306R: Guide to Cold Weather Concreting
- AASHTO T325: Standard Method of Test for Estimating the Strength of Concrete in Transportation Construction by Maturity Tests.
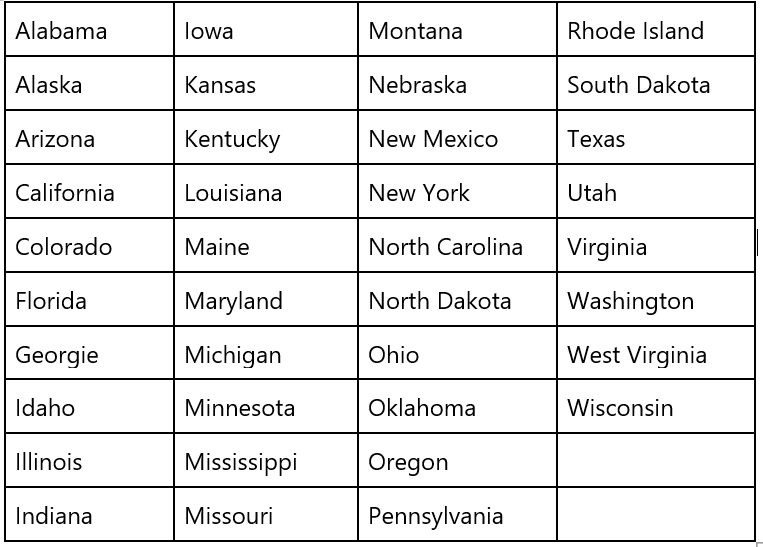
- DOT: The maturity method is widely adopted by most of the DOT’s in the United States. As of January 2018, 29 states accept maturity as one of the testing methods in their specifications. A list of those states is presented in the table below.
Canada
- CSA A23.1/A23.2: Concrete Materials and Methods of Concrete Construction/Test Methods and Standard Practice for Concrete
South America
- NCH 170: Hormigon- Requisitos generals (Concrete- General requirements)[37] Europe
Europe
Multiple European countries allow for the maturity method to be used as a measurement for in-place strength by specifying maturity in their own specific standards. The three standards that are generally used as a guide for measuring maturity:
- EN 206-1: 2002, Concrete – Part 1: Specification, performance, production and conformity BS EN 13670: Execution of concrete structures
- NEN 5970: Determination of Strength of Fresh Concrete with the Method of Weighted Maturity
If you don’t see your country listed above, check with the relevant governing body to see whether your country or region is working on standardizing the maturity method.
How to Calculate Concrete Maturity
There are several ways to calculate concrete maturity:
- Temperature-Time Factor
- Datum Temperature Calculation
- Rate Constant (K-Value)
- Equivalent Age
- Weighted Maturity
For projects that require easy-to-use and non-destructive tools, SmartRock is the world’s leading wireless sensor for the automatic monitoring of the curing and hardening of concrete based on the maturity method (ASTM C1074).












One Response
Any standards regarding IN INDIA