
Precisely monitor the temperature of your concrete structures under any conditions
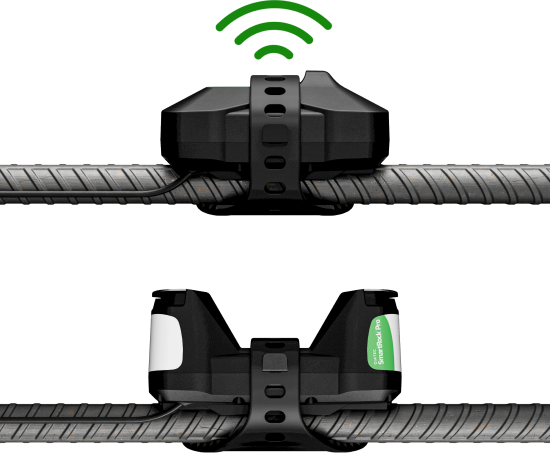

Collect real-time in-situ concrete strength data through maturity-based sensors
Maturity-Based Concrete Strength Monitoring
Self-Calibrating Concrete Strength Monitoring
AI-powered precision for every concrete mix for the Producers
Instant ROI
AI-Powered Decision Making
Drive Sustainability
Core Quality Control

Corrosion detection in concrete reinforcement
Concrete quality detection lab equipment





Experts revolutionizing the construction industry
Stay on the cutting edge of concrete tech
Save the date and join us at future events and conferences

In the world of construction, concrete mix design is often considered the art and science behind creating durable, high-quality concrete. Getting the right mix isn’t just about choosing materials; it’s about creating a formula that meets the specific demands of a project while ensuring long-term strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. In this blog, we’ll explore the essentials of concrete mix design in the UK discuss the challenges contractors face in achieving the perfect mix, and see how technology is making it easier to optimise concrete mix design for any project. What Is the Concrete Mix Design?Concrete mix design is the process of selecting and combining different materials—cement, water, aggregates, and admixtures—to create concrete that meets a project’s requirements. The aim is to create a mixture with the right balance of strength, workability, durability, and economy. In the UK, as in most regions, construction standards and codes (like the BS 8500-2) provide guidelines to ensure mixes meet minimum requirements for compressive strength, slump, and durability. However, every project has unique challenges, and achieving the optimal mix often requires careful adjustments.Interested in reading more about ensuring concrete strength and durability in the UK? Click here.Key Elements of Concrete Mix DesignCreating the right concrete mix is a…

When it comes to producing high-quality concrete, the importance of aggregate cannot be overstated. While most construction professionals focus on cement and admixtures, the shape of aggregates plays a crucial role in concrete performance. Two popular types of crushers—Jaw Crushers and Vertical Shaft Impact (VSI) Crushers—produce distinctly different types of aggregate. This blog dives into VSI vs. jaw crushers, their differences, and why VSI crushers could be the game-changer in optimizing your concrete mix.1. Understanding the Crushers Jaw Crushers: The Workhorse of CrushingJaw crushers are widely used in primary crushing. They rely on compression: two jaw plates move back and forth to crush large rocks into smaller fragments. While effective at reducing rock size, they tend to produce angular, flat, and elongated particles, often referred to as laminar aggregates. VSI Crushers: The Master of Shape VSI crushers, on the other hand, operate differently. By leveraging high-speed impact and rock-on-rock crushing mechanisms, they break down particles into more rounded and cubical shapes. VSI machines can work as both primary and secondary crushers, giving them versatility.2. The Shape Factor: Why It Matters Cubical vs. Laminar Aggregates Impact on Workability Concrete with cubical aggregates is more flowable, requiring less paste to achieve desired slump levels. This reduces water and…

In the UK, concrete testing is a critical part of construction, and British Standards provide the framework for ensuring quality, safety, and compliance. For contractors and engineers, understanding and adhering to these standards is crucial—not only for the integrity of a structure but also for meeting regulatory requirements and avoiding costly rework. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at some of the most relevant British Standards for concrete testing, the challenges contractors often face with compliance, and how technology is helping to streamline the process.What Are British Standards for Concrete Testing? British Standards (BS) are a series of guidelines and specifications developed to maintain high standards across industries in the UK. For concrete testing, these standards cover everything from the materials used in concrete mixes to the methods for testing strength, durability, and workability. They ensure that the concrete used in construction is safe, durable, and capable of withstanding expected loads and environmental conditions. The two most commonly referenced British Standards for concrete testing are:Read our blog on concrete cube testing in the UK. Click here!Why Is Adhering to British Standards Important?Meeting British Standards is essential for several reasons: The Challenges of Meeting British Standards While British Standards provide a roadmap for quality…
Visit our careers page to learn about our award-winning culture and our open positions.