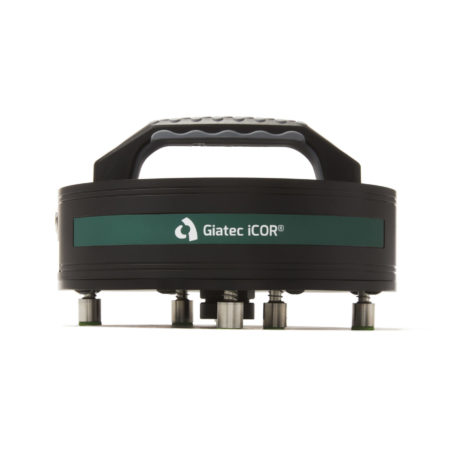
iCOR®
Wireless NDT Corrosion Detection
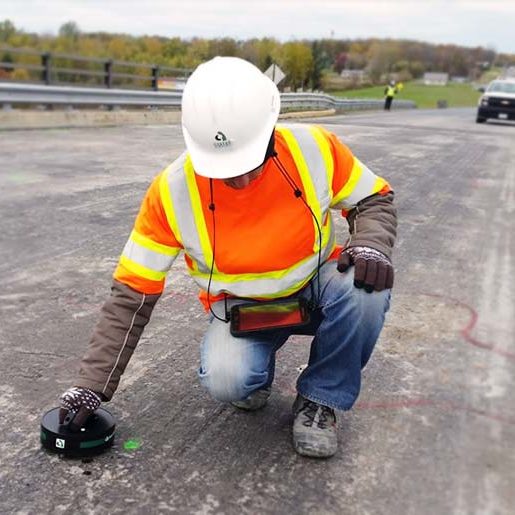
A device for evaluating and measuring the rate of rebar corrosion in seconds
iCOR®
A device for evaluating and measuring the rate of rebar corrosion in seconds

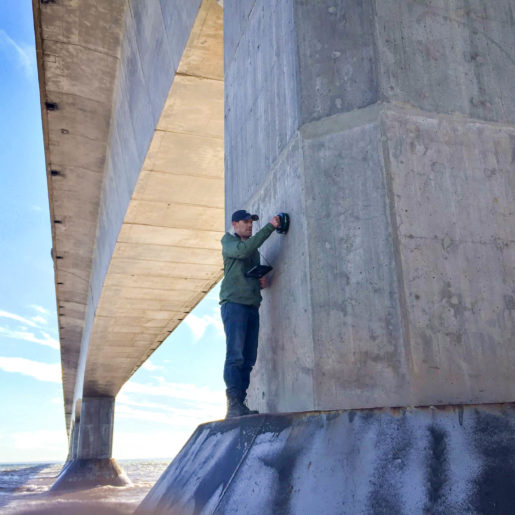
Unlike other devices which must drill into the concrete and physically connect to the rebar to evaluate corrosion, the iCOR® is completely non-destructive.
Data is collected, analyzed, and stored wirelessly within the mobile app on the tablet provided where it can be easily shared with team members.
Detailed corrosion evaluation of reinforced concrete structures is presented as contour maps which are accessible in real-time on the tablet.

iCOR is the most advanced wireless corrosion measurement device for evaluating the health of reinforced concrete structures. iCOR detects corrosion potential, corrosion rate, and in-situ electrical resistivity. In 2019, the iCOR was presented the Corrosion Innovation Award by the National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE).
Find the right corrosion detection solution for your concrete testing needs!
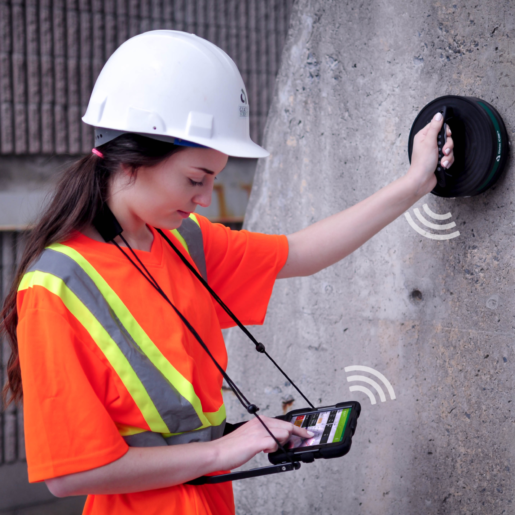
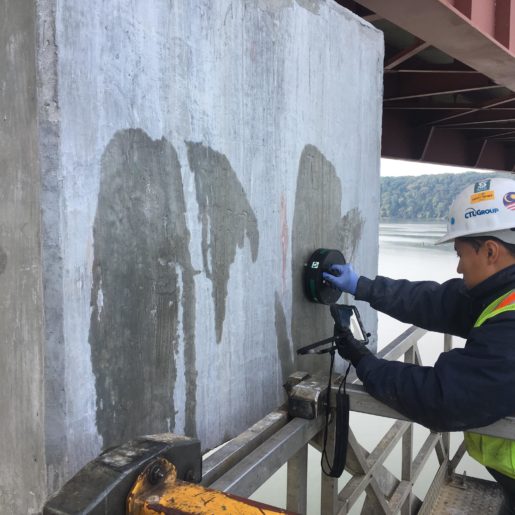






ASTM C876 – Standard Test Method for Corrosion Potentials of Uncoated Reinforcing Steel in Concrete
Patented Technology
iCOR benefits from the patented CEPRA technology that makes it possible to estimate the rate of rebar corrosion through a noninvasive, non-destructive approach. This means that the need to connect the device to the rebar to obtain measurements, which is the case for other commercial devices, is eliminated with the iCOR.
| Testing Time | 3 to 30 seconds |
| Corrosion Rate Range | 0 to 500 μm / year |
| Corrosion Potential Range | -800 to +200 mV / CSE |
| Electrical Resistivity Range | 0 to 10,000 Ω • m |
Additional resources on concrete corrosion:
| Part No. | Item | Description |
| 900081 | iCOR | Beta unit, Tablet with hands-free carrying support, Data Analysis App., User manual, Connection sponges, USB cable, Conductive solution, Carrying Case. |
There is no standard available yet for the corrosion rate measurement based on the patented CEPRA technique. Giatec iCOR is the only product on the market that does not require the connection to the reinforcement to obtain corrosion rate. In addition to corrosion rate and resistivity, the iCOR also provides a standard half-cell measurement unit for corrosion potential measurement; the half-cell measurement is optional as it requires connection to the reinforcement. The standard for corrosion potential measurement of rebar in concrete is ASTM C876.
The user needs to input the cover thickness in the software for corrosion rate measurement. The range of cover thickness can vary from 0.4 to 3.5 in (1 cm to 9 cm) with an increment of 0.4 in (1 cm).
iCOR measurements are sensitive to the concrete moisture. The dryer the concrete is, the higher the electrical resistivity values, the lower the corrosion rate and more positive the corrosion potential will be. Pre-wetting the concrete surface is required before the use of any corrosion measurement. In the case of iCOR, a wet connection between the electrodes and surface of concrete through sponges is required to obtain reliable measurements.
The iCOR uses a solid-base Ag/AgCl electrode for the half-cell measurement. This is a maintenance- free electrode capable of doing upside down measurement and less prone to contamination due to chlorides. Ag/AgCl has a fixed potential offset compared to the Cu/CuSO4 electrode; the iCOR software accounts for this difference and presents the results in mV/CSE (i.e. Cu/CuSO4 Electrode) as per the ASTM C876.
The iCOR applies an electrical current between the two outer electrodes; any non-conductive layer will cause interruption in the flow of current into concrete. If the epoxy on the bar is perfectly intact, no measurement would be possible.
What is the battery life of the device?
The iCOR battery will last a full day of use, simply make sure it is fully charged the night before. The unit roughly takes 4 hours to charge. The tablet will indicate the level of battery life on the unit at all times. We also recommend having the tablet charged the night before, the tablet will have the limiting battery life in the package (similar to a phone). In addition, it is possible to utilize an external battery pack that can be used to mitigate the battery consumption of the tablet.
What are the limitations of the device?
In general, any feature in the reinforced concrete structure that breaks electrical continuity at the point of measurement will not permit testing, i.e. epoxy coated/galvanized rebar, tensioning ducts sheathing (plastic), asphalt wearing surfaces/waterproofing, fiber reinforced concrete. This is not a limitation of the iCOR but applies to all corrosion detection devices.
Some other aspects of the analyzed structure might affect the readings, such as the presence of voids/ large cracks. As a rule, any nonconductive layer or air layer will block the current from reaching the reinforcement. Another limitation that you may encounter in your region is the temperature measurement range. There is no corrosion activity in the sub 0°C (32°F) temperature as the water inside the concrete becomes ice, it drastically changes the concrete resistivity behavior which would impact the results. Those are not limitations of our equipment but limitations of corrosion rate measurement in general.
What is the minimum and maximum cover depth for inspection?
A minimum of 10 mm is recommended as the minimum cover depth for inspection. 90 mm is the maximum rebar cover allowable for the iCOR to perform an accurate measurement. Moreover, the equipment will always read the first rebar layer, so if the intent is to read the rebars that are on other layers, the current will be drawn toward the first rebar layer only. When using the corrosion potential, the greater the cover depth, the lower that reading signal gets. Using the half-cell potential on cover depths >90 mm, the interpretation of the results must be carefully made as small differences can represent local corrosion.
Should corrosion rate measurements be performed if the rebar has corroded severely and the diameter has decreased drastically?
In that situation, the concrete itself would demonstrate significant signs of corrosion. If the corrosion process is severe enough to reduce drastically the rebar diameter, its expansion will deteriorate the concrete, and mapped cracks and delamination will appear on the concrete surface. The primary goal of the equipment is to identify corroding rebars that did not yet severely damage the concrete and take actions to prevent further deterioration.
Are there any recommendations to perform corrosion rate and corrosion potential measurements at the same time?
If it is decided to make a 3 in 1 measurement with the iCOR, when pressing the measurement button, first a half-cell measurement will be taken, followed by both the electrical resistivity and corrosion rate simultaneously. The corrosion rate and electrical resistivity measurement will polarize the reinforcement therefore the half-cell measurement needs to be performed first at a specific location. The iCOR only polarizes the rebar for a short period of time, when the measurements are set to 3, 6 or 10 seconds, however it is always recommended to wait at least 30 minutes before repeating a measurement at the exact same location.
How should the surface of the concrete be prepared before a corrosion rate measurement?
It is highly recommended to pre-wet the surface of the concrete before the measurement is taken as described in ASTM C876. The ideal condition to perform a test is in a saturated surface dry (SSD) condition. This is, however, sometimes hard to achieve on site. Ponding the surface before the test is a very good preparation step. If ponding is used, make sure the excess water on the surface dries or gets removed before the test as excess running water between the surface of the concrete and the iCOR electrodes will cause errors in the measurements.
What is the minimal spacing between the rebars?
There is a limitation to the spacing of the rebar, which is related to the two voltage response electrodes located at the center of the device. If there are two sections of rebar passing through these electrodes, the results will not output correctly. So, the limitation spacing is around 10 cm or 4 in.
For rebars near the edge of the concrete element, are there any limitations?
As long as the 4 electrodes in the measurement direction make contact with the concrete surface on top of the reinforcement, it will be possible to perform a measurement. For example, in the y-direction (handle direction) the current is passed through the outer two electrodes, and the voltage response is measured by the inner electrodes. This statement also applies to the curve surfaces (e.g : columns).
What is the benefit of taking half-cell and corrosion rate measurements together?
With the iCOR, it is possible to perform different types of measurements together or independently (refer to user manual for more information). The five types of measurements are:
1 – Corrosion rate (includes concrete resistivity)
2 – Corrosion rate (includes concrete resistivity) and half-cell potential
3 – Half-cell potential
4 – Concrete resistivity
5 – Half Cell potential and concrete resistivity
Half-cell is included in the unit because it is the only standardized corrosion method. It provides a qualitative measurement while the corrosion rate provides a quantitative assessment. The user tends to use both measurements in the earlier test and move away from half-cell because the results obtained from corrosion rate can be correlated. The iCOR is capable of measuring corrosion rate and concrete resistivity without a connection to the reinforcement, but requires one for the half-cell test.
Is it necessary to use a cover meter/rebar locator to identify the rebar location?
Yes, it is necessary to use a rebar detector/ cover meter to localize the rebars before the test. The iCOR must be aligned with the reinforcement. Location of the rebar, cover depth, and size of the reinforcement are all mandatory information that need to be inputted in the iCOR software.
Does the iCOR require a connection to the reinforcement during the test?
Only when the device is used to measure corrosion potential (HCP). If the device is used for corrosion rate and/or electrical resistivity assessment only, the connection to the reinforcement is not necessary.
Does the half-cell electrode need to be calibrated?
A verification probe is available upon purchasing any iCOR package. It is recommended to verify the device using the reference electrode before conducting corrosion potential mapping. The half-cell doesn’t require calibration, but must be maintained in good condition in order to pass the verification.
Can the device develop corrosion mapping for non-flat surfaces?
Yes, corrosion maps can be developed for a non-flat surface, the tablet application creates a grid which represents plan surface. In the case of non-flat testing surfaces, for example a column, the measurements taken on the circumference are represented as a surface. The user creates a grid with desired dimension and spacing and measurements can be taken at any location within that grid.
However, in the presence of a non-plan surface, it is important to ensure that all the four electrodes in the measurement direction selected for electrical resistivity and corrosion rate be in contact with the concrete surface.
How to wet the surface?
The best condition is saturated surface dry (SSD). This condition can be achieved by wetting the surface with a water spray, water hose, sprinkler, pounding the surface, etc. Wet the surface as much as possible and let it dry for 15-20 minutes before the measurement is taken, making sure there is no running water on the surface of the concrete.
Watch how SmartRock can work for you.